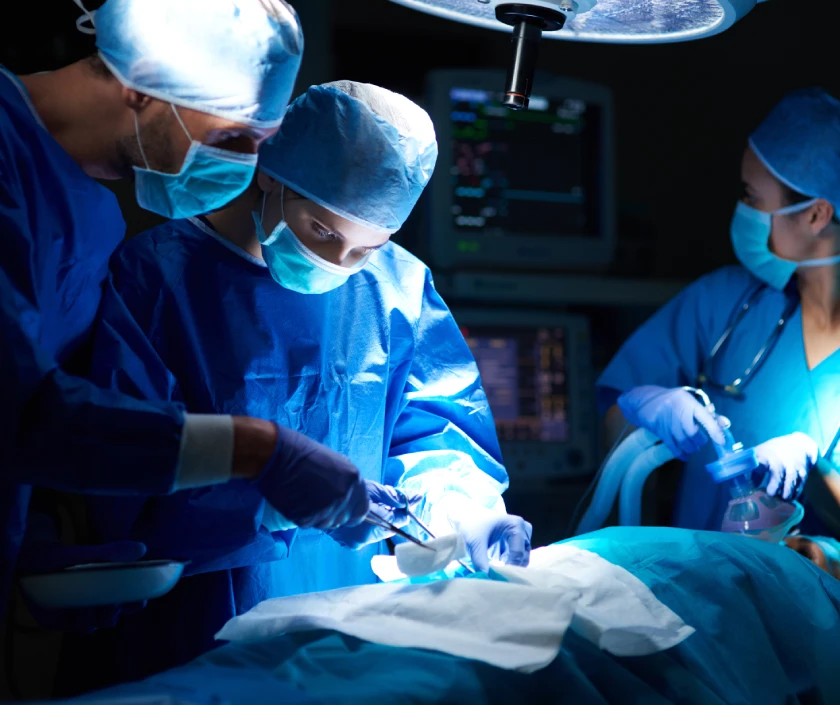
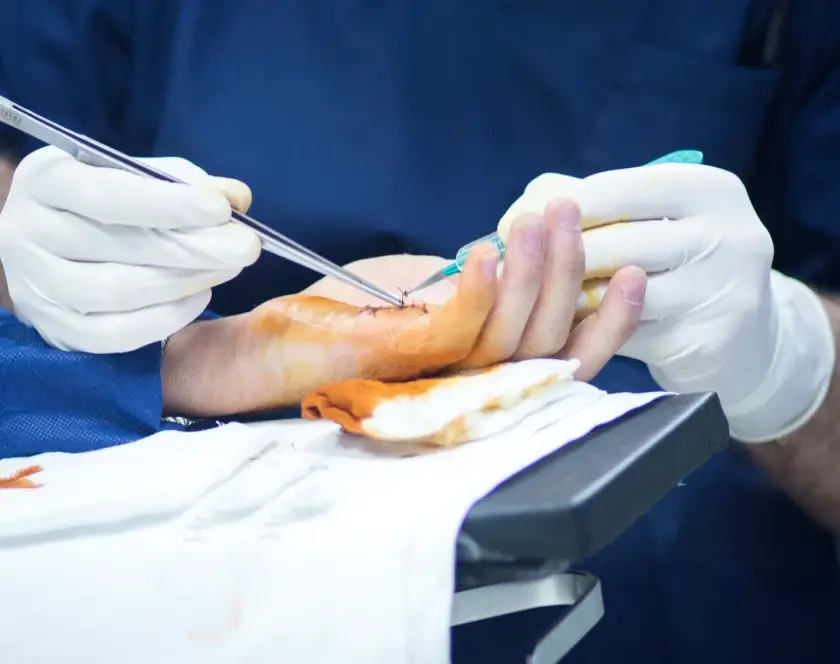
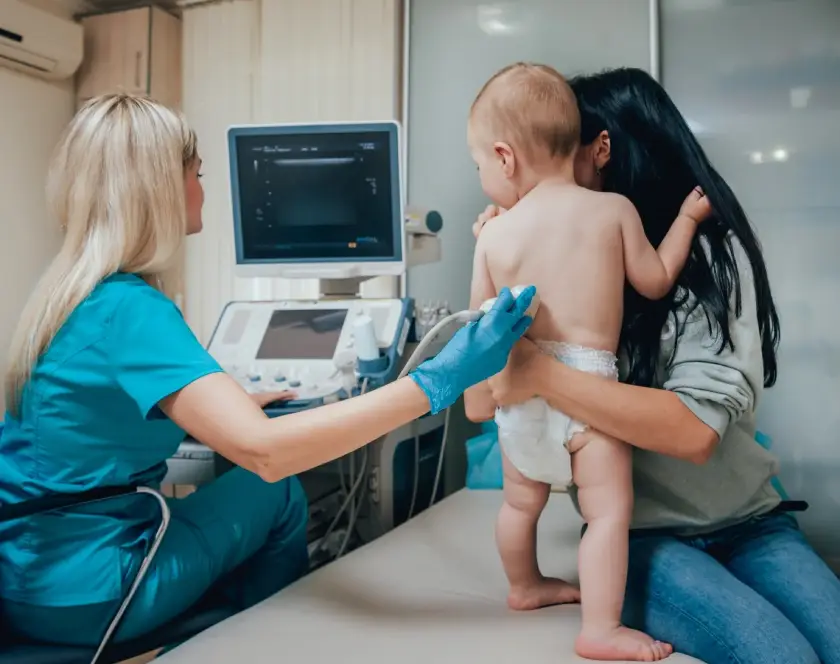
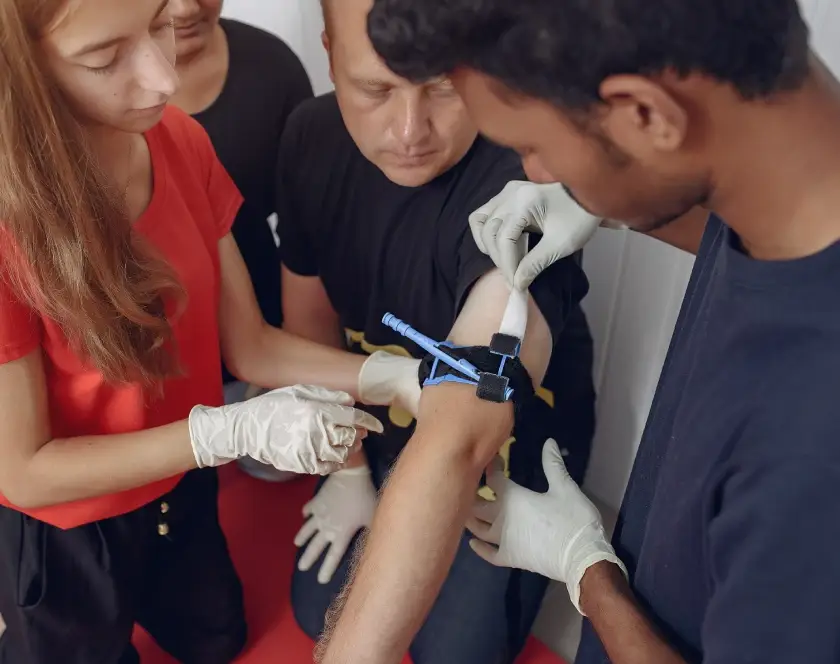
What is Head and Neck Reconstruction?
At Elegance Clinic, we specialise in microvascular surgery, an advanced reconstructive technique that uses high-precision surgical microscopes to repair or restore blood flow in tiny blood vessels. This enables reattachment of amputated parts, revascularisation of injured tissues, and free tissue transfers to rebuild areas damaged by trauma, burns, or cancer.
What is Microvascular Surgery?
Microvascular surgery involves connecting blood vessels that are often less than 3 millimetres in diameter using fine sutures under a microscope. This highly specialised procedure restores circulation and tissue viability, making it possible to save body parts that would otherwise be lost.
Types of Microvascular Surgery We Perform
Replantation
Replantation refers to the surgical reattachment of a completely amputated body part. It involves meticulo seus repair of bones, tendons, nerves, arteries, and veins under a microscope to restore function and appearance. Replantation is most commonly performed for hand, finger, and thumb injuries resulting from industrial, household, or road traffic accidents. In such cases, early surgical revascularisation is critical to restore blood flow and ensure the survival of the replanted part. By combining microsurgical techniques with advanced rehabilitation, replantation enables patients to regain movement, strength, and sensation in their amputated hand, finger, or thumb, significantly improving their quality of life. At Elegance Clinic, our microvascular surgeons specialise in surgical revascularisation and replantation procedures, ensuring optimal outcomes even in complex trauma cases. Prompt surgical intervention and expert care can make the difference between permanent disability and a functional, pain-free limb.
Replantation refers to the surgical reattachment of a completely amputated body part. It requires meticulous repair of bones, tendons, nerves, arteries, and veins to restore function.
- Hand, finger, and thumb replantation: Injuries to fingers and thumbs are common in industrial accidents. Early surgical intervention improves chances of survival and function.
- Lower limb replantation: Leg or foot replantation restores mobility and avoids permanent disability.
- Elbow replantation: Rare but possible with microvascular repair techniques.
- Penis replantation: Performed in specific traumatic injuries to restore both function and appearance.
- Foot replantation: Helps regain ambulation and prevents the need for prosthetics in suitable cases.
Revascularisation
Revascularisation is a critical microvascular surgery procedure used to restore blood flow to an injured or compromised body part, preventing tissue death and preserving function. When surgical revascularisation alone is insufficient due to extensive damage or loss of tissue, free tissue transfer becomes essential. Free tissue transfer involves moving skin, muscle, bone, or a combination flap from another part of the body to the affected area, with microvascular anastomosis performed under a microscope to re-establish circulation. This advanced technique is crucial in reconstructing hand, finger, and thumb injuries caused by severe trauma, crush injuries, or cancer excision, where local tissues are inadequate for coverage. By providing well-vascularised tissue to cover exposed bones, tendons, or joints, free tissue transfer enhances healing, preserves limb length, and restores function. At Elegance Clinic, our expertise in surgical revascularisation and microvascular free tissue transfer ensures optimal aesthetic and functional outcomes for our patients.
Revascularisation involves microvascular repair to restore blood flow to an injured or partially severed body part without complete detachment.
- Finger, thumb, and hand injuries where circulation is compromised due to trauma or crush injuries.
- Other body parts that require vessel repair to prevent tissue death and loss of function.
Free Microvascular Tissue Transfer
Free tissue transfer is a vital microvascular surgery technique that involves moving skin, muscle, bone, or a combination flap from one part of the body to another. Through microvascular anastomosis, blood vessels of the flap are connected to vessels at the recipient site under a microscope to restore circulation. This procedure is crucial in trauma, burns, and cancer reconstruction, where local tissues are insufficient. In hand, finger, and thumb reconstruction, free tissue transfer restores form and function after severe injuries or tumour removal, allowing patients to regain mobility and dexterity. It is also used when surgical revascularisation is not possible due to extensive tissue loss, as the free flap provides healthy, well-vascularised tissue to cover exposed bones, tendons, or joints. Commonly used flaps include the radial forearm flap, fibula flap, and anterolateral thigh flap. These techniques ensure optimal healing, preserve limb length, and improve overall aesthetic and functional outcomes for patients.
- Trauma reconstruction: Repairing large wounds or defects following severe injuries.
- Burn reconstruction: Rebuilding areas with extensive skin loss.
- Cancer reconstruction: Restoring form and function after cancer removal surgeries.
- Free ALT flap (Anterolateral Thigh Flap): A Versatile flap with a long vascular pedicle used for soft tissue coverage.
- Free fibula flap: Ideal for reconstructing jaw bones or long bone defects.
- Free radial forearm flap: A Thin, pliable flap suitable for head, neck, and hand reconstructions.
Vasoplasty and Tubal Recanalisation
- Vasoplasty: Microsurgical reconstruction of the vas deferens for male infertility management.
- Tubal recanalisation: Reversal of female sterilisation procedures to restore fertility using microvascular techniques.
Who Needs Microvascular Surgery?
- Individuals with amputated fingers, thumbs, or limbs due to accidents.
- Patients with severe crush injuries leading to compromised blood flow.
- Cancer patients need reconstructive surgeries after tumour removal.
- Those seeking sterilisation reversal to restore fertility.
Why Choose Elegance Clinic for Microvascular Surgery?
- Expertise: Our reconstructive surgeons are trained in advanced microvascular techniques, ensuring high success rates.
- Microsurgical setup: Equipped with state-of-the-art operating microscopes and instrumentation.
- Comprehensive care: From emergency replantation to planned free flap transfers, we offer integrated surgical and rehabilitation services.
- Patient-centred approach: Compassionate pre-operative counselling and post-operative support for functional recovery.
Hear from our patients
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I would like to thxnamrata for skin care she has done wonderful job I really appreciate her thx namrata once againPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Very good service Sp. Thanx namrata benPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I had an excellent experience at Elegance Clinic for my hair transplant. The entire team was very professional, supportive, and reassuring throughout the process. Everything was clearly explained in detail, from the initial consultation to the procedure itself and the post-operative care. Pre-operative preparation was thorough, intra-operative care was meticulous, and post-operative guidance was clear and well structured. The procedure was completely painless, both during and after surgery, which was very reassuring. Overall, the care was of a very high standard, and the experience exceeded my expectations. I would highly recommend Elegance Clinic to anyone considering a hair transplant.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I had Q-Switch laser treatment done by Dr. Ashutosh Shah at Elegance Clinic. Very satisfied with the treatment and results. Doctor and staff were professional and supportive.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Thank you so much dearest dr.ashutosh shah and ur best team for the treatment....we r really grateful to uPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I had a really good experience with Elagnace clinic. I got my ear piercing done. It was my first ever piercing and it went really well. Painless and really handles with care. Shoutout to the whole team who relaxed me during the procedure. Everyone over here had a great positive attitude. Highly recommend them. 😊Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I underwent dermabrasion at Elegance Clinic by Dr. Ashutosh Shah, and the results are amazing. The procedure was explained clearly, and I felt comfortable throughout. My skin looks smoother and healthier now. Very satisfied with the treatment and care.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best result per wait bohut krvate haiPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I got face microneedling done at Elegance Clinic with Dr. Ashutosh Shah and had a very positive experience. Dr. Shah and the team are professional, knowledgeable, and friendly, explaining the procedure clearly and making me feel comfortable throughout the session. The clinic is clean, well-organized, and hygienic, and the staff is supportive and attentive. I’m happy with the results and would recommend Elegance Clinic for microneedling and other skin treatments.
Contact Us
Ready to discuss? Fill out our contact form for a confidential consultation.
FAQ
What is microvascular surgery?
Microvascular surgery is an advanced surgical technique that uses a microscope to repair or connect tiny blood vessels, usually less than 3 millimetres in diameter. It is crucial in hand, finger, and thumb reconstruction, surgical revascularisation, and free tissue transfer procedures, where restoring blood flow is essential to save or rebuild body parts after trauma, burns, or cancer surgery.
What is the success rate of microvascular surgery?
The success rate of microvascular surgery is high, ranging from 90-98%, depending on factors like the patient’s health, timing of surgery, and severity of injury. In hand, finger, and thumb surgical revascularisation or replantation, early intervention by an experienced microvascular surgeon significantly improves outcomes, preserving function and appearance.
How long does microvascular surgery take?
Microvascular surgery can take 4 to 12 hours or longer, based on the complexity of the procedure. For example, hand, finger, and thumb surgical revascularisation or replantation may require several hours to meticulously repair bones, tendons, nerves, and blood vessels under a microscope for optimal results.
What is meant by vascular surgery?
Vascular surgery refers to procedures performed on arteries and veins to treat conditions like blockages, aneurysms, or injuries affecting blood flow. Microvascular surgery is a specialised branch that focuses on repairing very small vessels, commonly used in surgical revascularisation and free tissue transfer for hand, finger, and thumb reconstruction to restore circulation and tissue viability.