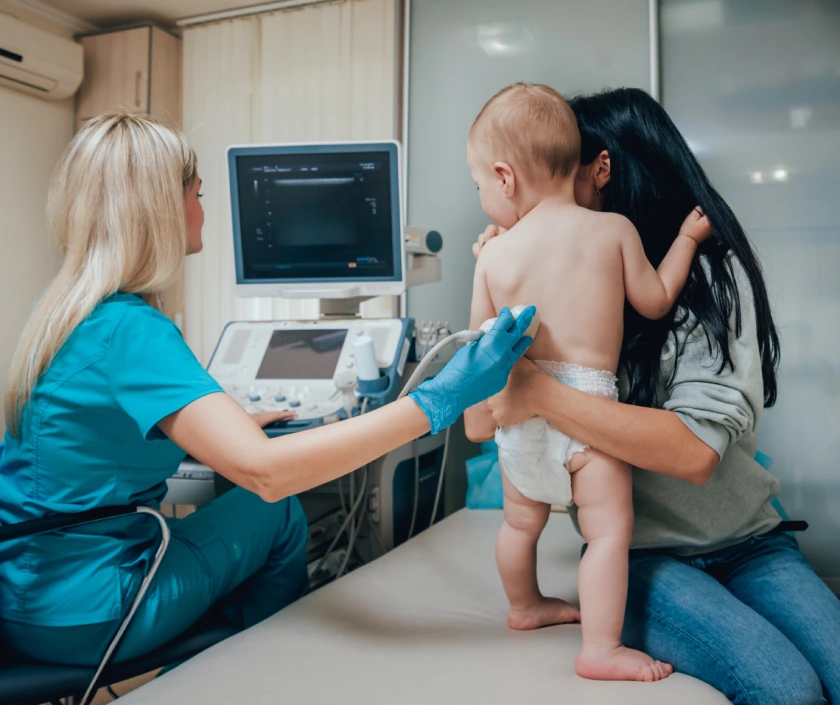
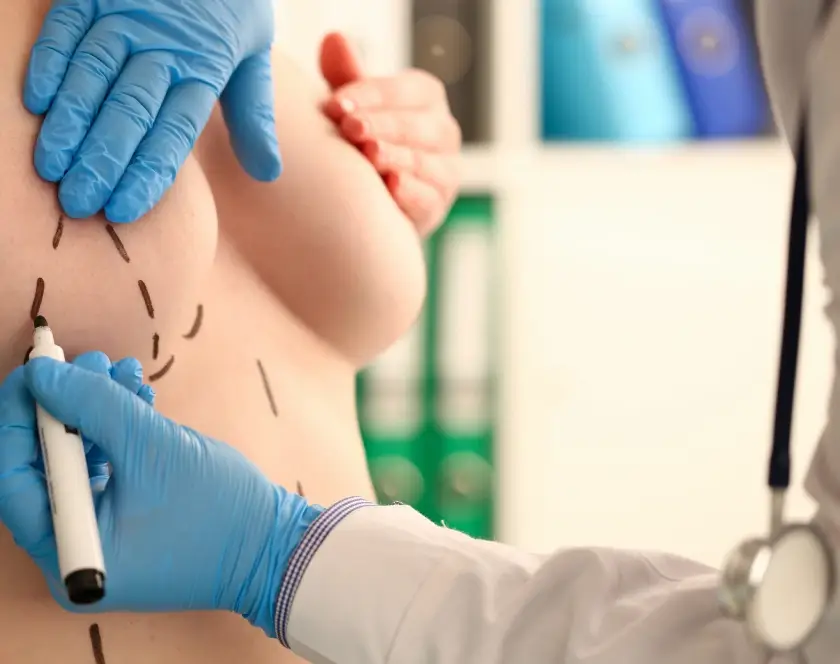
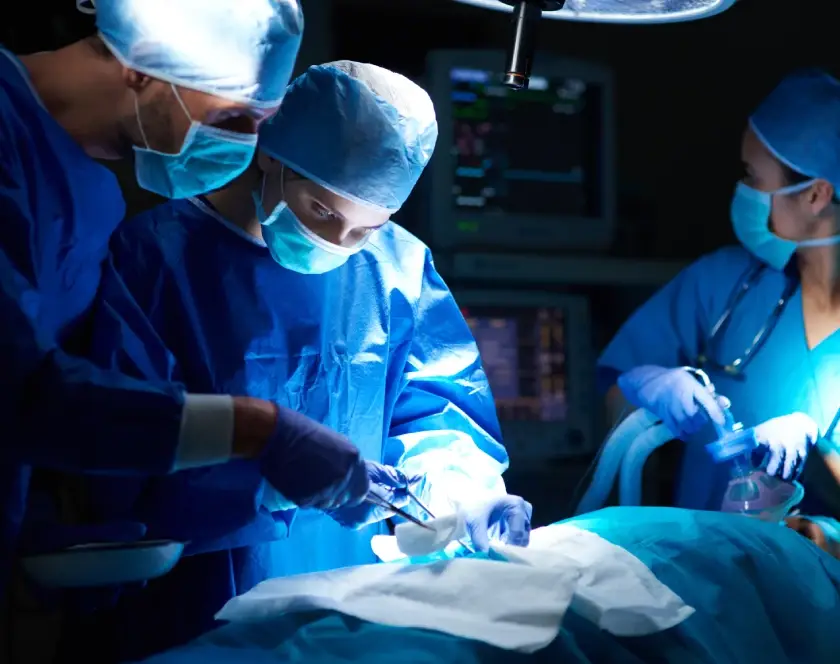
Congenital anomalies, also called birth defects, are structural or functional abnormalities present from birth. These may affect facial features, limbs, genitals, spine, or internal organs and can impact function, appearance, or both.
At Elegance Clinic, we offer comprehensive evaluation and surgical correction of various congenital deformities through highly specialised reconstructive plastic surgery. Our goal is to improve both physical outcomes and emotional well-being.
When Is Treatment for Congenital Anomalies Needed?
Surgical or medical care is recommended when anomalies cause:
- Feeding or speech difficulty
- Restricted limb function
- Urinary or genital issues
- Aesthetic concerns affecting confidence
- Increased risk of infections
- Social or psychological challenges
Types of Congenital Anomalies and Conditions Treated
Facial and Oral Deformities
- Cleft lip, palate, and nose deformity
- Types of facial clefts, like bilateral or unilateral
- Congenital anomalies of the nose
Hand and Finger Anomalies
- Syndactyly (fused fingers)
- Polydactyly (extra fingers)
- Clinodactyly (curved finger)
- Macrodactyly (enlarged finger)
- Amniotic band syndrome
- Auto-amputation of digits
- Radial club hand
Penile and Urethral Anomalies
- Hypospadias and Epispadias
- Congenitally short urethra
- Buried penis
- Undescended testes
- Phimosis
- Small penis
- Bifid scrotum
- All classified under penile congenital anomalies
Spinal Cord Defects
- Reconstruction of Meningomyelocele
- Correction of abnormal hair growth over the spine
Ear Anomalies
- Anotia, Microtia (underdeveloped or absent ear)
- Lobe ear, Bifid ear lobe
- Preauricular sinus
- AV malformation (arteriovenous malformation)
Muscular Deformities
- Torticollis (twisted neck)
- Spastic muscles in children
Neurovascular Deformities
- Haemangioma (vascular birthmark)
- Vascular malformations: arterial or venous
- Neurofibroma, Plexiform neurofibroma
Tongue and Facial Movement Issues
- Tongue tie (ankyloglossia)
- Facial nerve deficit
- Syndromes like Treacher Collins, Craniosynostosis, and Hemifacial microsomia
Pre-Treatment Protocol
Each patient undergoes:
- Detailed physical examination and diagnosis
- Imaging or genetic workup if needed
- Growth and functional assessment
- Parent counselling and pre-op preparation
- Surgical planning with a multidisciplinary team
Treatment Process: How We Manage Congenital Anomalies
- Cleft lip/palate repair with aesthetic and speech improvement
- Hand anomalies surgery for better grip and motion
- Genital reconstruction for urinary and cosmetic correction
- Ear reshaping (otoplasty) or ear framework reconstruction
- Excision of vascular tumours or laser therapy for haemangiomas
- Microsurgery for neurovascular malformations
- Release of tongue tie for better speech and feeding
- Spinal defect reconstruction to prevent neurological decline
- Facial bone reshaping in syndromic conditions
Duration of Treatment
- Most surgeries take 1–4 hours
- Hospital stay: 1–3 days, depending on complexity
- Multiple stages may be required for some deformities
- Full functional recovery: varies by condition (2 weeks to 6 months)
Clinical Considerations: Risks and Benefits
Risks:
- Bleeding or infection
- Scar formation
- Need for revision surgery
- Growth-related recurrence (in children)
Benefits:
- Improved function (speech, grip, urination)
- Enhanced appearance and confidence
- Better social and developmental outcomes
- Reduced risk of complications in adulthood
Aftercare Instructions
- Follow wound care protocol
- Use prescribed medications and creams
- Attend all follow-up visits
- Physiotherapy or speech therapy, if advised
- Monitor growth milestones and development
Recovery Timeline
- Minor soft-tissue surgeries: 2–3 weeks
- Skeletal or complex deformities: 2–6 months
- Multi-stage cases may extend over a year
- Long-term monitoring is recommended until adolescence
When to Consult for Congenital Anomalies?
You should consult a specialist at Elegance Clinic if your child shows:
- Abnormal face, limb, genital, or ear development
- Difficulty in feeding, urination, or speech
- Unusual growths or vascular spots
- Signs of spinal or muscular deformities
Hear from our patients
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr.shah is very kind and understanding... during my surgery of xentholesma..sir didn't late me feel nervous at all..he kept talking to me..he kept singing classic old hindi songs while performing surgery..I was like "ye to apne type ka banda hai"..I didn't even realise when my surgery got over. mr. Bhargav in staff and other team members were very kind an supportive.. I just have one minor complaint..simple panipuri wala or vegetable person in surat is always ready to receive online,UPI ,QR payment..but,pharmacist over their always be like "mera to cash payment hoga". Rest all is good.. people over there are very sincere at their work. I would definitely suggest to visit elegance clinic for getting your xentholesma cured.treatment charges are also affordable.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I am fully satisfied my hydrafacial treatmentPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. The experience was too good staff was really humble and the results were actually good!Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I got hair transplant which is very painful but Got it done on ELEGANCE so it was very normal and which was bery helpful for me Special thanks to staff.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I had PRP and laser treatments at Elegance clinic for my skin and hair, and the experience has been truly excellent. Dr. Krina handled my skin treatment with great care and attention — I noticed a visible improvement in my skin texture and glow. For my hair, Dr. Bhargav and Dr. Ashutosh guided me through the PRP sessions with patience and professionalism, ensuring I was comfortable and well-informed throughout. The entire staff is polite, supportive, and the clinic maintains high standards of hygiene and advanced equipment. Overall, I’m very satisfied with the results and would highly recommend this hospital to anyone looking for genuine care and effective treatmPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr Asutosh sir is very excellent Tammy tack sargary..Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. A good doctor clinic review often highlights a clinic's positive aspects, such as a doctor's expertise, a friendly and competent staff, convenient hours, and a clean, comfortable environment.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. After suffering a serious burn injury due to a machine accident, I was fortunate to be treated by Dr. Ashutosh Shah at Elegance Clinic. His skill and calm approach gave me confidence from the first consultation. The surgery was done with great care, and the recovery support was outstanding. The clinic is clean and peaceful, and the staff treats you like family. Forever thankful for their help during a very tough timePosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. One of the best doctors as well as staff in the town, just loved the process post surgery, follow up calls is non negotiable for them. Dr ashutosh shah and dr chetan were incredible. Best service provided by the elegance clinic!Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. "We had a wonderful experience at Elegance Clinic for my wife's HIFU treatment. The staff was friendly and supportive, and the clinic environment was very professional. Dr. Ashutosh Shah took the time to explain the procedure and what to expect. The final result is excellent—my wife's skin looks much firmer and rejuvenated. She is very happy, which makes me happy! A truly world-class clinic for aesthetic procedures
Contact Us
Ready to discuss? Fill out our contact form for a confidential consultation.
FAQ
What is a congenital anomaly called?
A congenital anomaly is a birth defect or developmental disorder present at or before birth. These can affect various parts of the body, including the face, limbs, genitals, or internal organs, and may impact appearance or function.
How to avoid congenital abnormalities?
Some steps that can help reduce the risk of congenital anomalies include:
- Avoiding alcohol, tobacco, and harmful medications during pregnancy
- Ensuring adequate prenatal nutrition and folic acid intake
- Getting vaccinated and avoiding infections during pregnancy
- Attending regular prenatal check-ups
- Undergoing genetic screening if there’s a family history of anomalies
What are the four main causes of birth defects?
- Genetic abnormalities (inherited or spontaneous mutations)
- Environmental exposures (chemicals, radiation, drugs)
- Maternal infections during pregnancy (e.g., rubella, Zika)
- Nutritional deficiencies (e.g., lack of folic acid)
What are 10 serious complications of pregnancy?
Pregnancy complications that may impact both mother and child may include:
- Preterm labor
- Preeclampsia
- Gestational diabetes
- Fetal growth restriction
- Placenta previa
- Congenital anomalies
- Maternal infections
- Miscarriage
- Vaginal or uterine bleeding
- Fetal distress
What is the most common cause of congenital anomalies?
The most common causes of congenital anomalies are usually genetic abnormalities and environmental factors (e.g., teratogens during pregnancy).